This article was originally published on 𝕏.
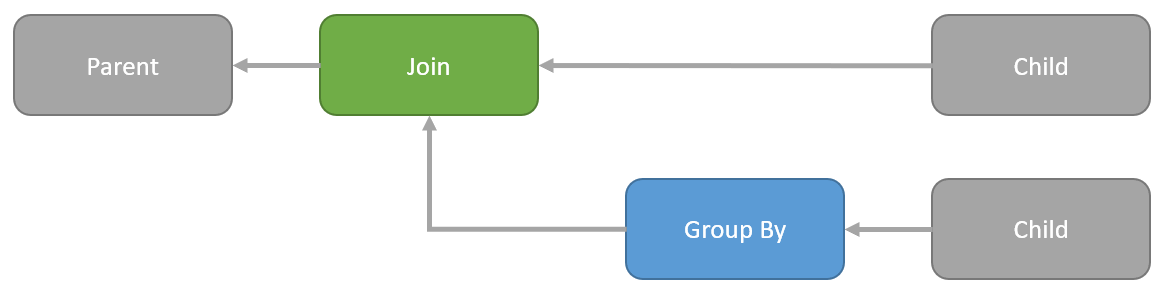
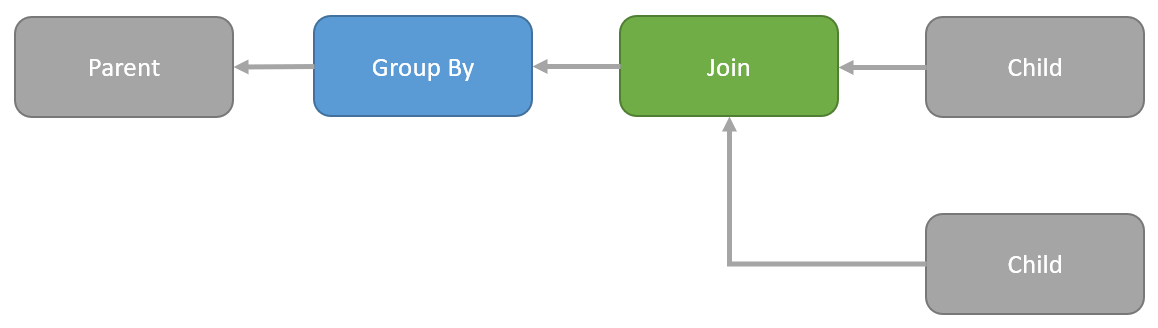
I was asked recently why Halloween Protection was needed for data modification statements that include a self-join of the target table. This gives me a chance to explain, while also covering some interesting product bug history from the SQL Server 7 and 2000 days.
If you already know all there is to know about the Halloween Problem as it applies to SQL Server, you can skip the background section.